Dwarf Water Lettuce vs Frogbit is two standard options for aquarium owners and amateurs in aquatic plants. These plants assist aquatic environments in various ways, including giving fish cover and shade, minimizing algal growth, and enhancing water quality. However, given their many similarities, it can be difficult to choose among them.
Today I will explain the distinctions between Dwarf Water Lettuce and Frogbit to assist you in choosing which is the greatest fit for your aquatic setup.
6 Key differences while comparing Dwarf Water Lettuce vs Frogbit
Here is a list of 6 key differences while comparing these two together:
- Origin
- Leaves Difference
- Roots difference
- Difference in Flowers
- Growth rate differences
- Maintenance requirement
Dwarf Water Lettuce and Frogbit: Origins
Dwarf water lettuce is native to South America and is commonly found in slow-moving water bodies, such as ponds, ditches, and marshes. In many regions of the world, including the United States, this plant is regarded as an invasive species because it can obstruct streams and disrupt local ecosystems.
On the other hand, Frogbit is native to Europe and Asia and is commonly found in still or slow-moving water bodies, such as ponds and lakes. In contrast to Pistia Stratiotes, Frogbit is not regarded as an invasive species and is a common plant in ponds and aquariums all around the world.
Dwarf Water Lettuce vs Frogbit: Leaves
Dwarf Water Lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) is a green, rosette-forming plant with round, cabbage-like leaves. The leaves have a velvety texture and reach as much as 0.5-1 inch with no stem. However, they can grow quite large and can be up to 10 inches wide.
Although the leaves normally have a bright green tint, the lighting and water conditions may cause them to alter significantly.

Frogbit, on the other hand, has lengthy, lily-pad-like leaves that are round or heart-shaped (Limnobium laevigatum). With a length of 0.5-2.0 inches, Frogbit leaves are often longer than those of Pistia Stratiotes. The leaves have a glossy, smooth surface and are flat as well.
Why is the variation in leaf form significant? How a plant absorbs light and nutrients depends on the form of its leaves. Because Pistia Stratiotes has round leaves that maximize light absorption, the plant is frequently used in aquariums with low lighting.
However, Frogbit has flat leaves that maximize surface area, which makes it simpler for the plant to absorb extra nutrients from the water.
Dwarf Water Lettuce vs Frogbit: Roots Differences
Small and floaty, dwarf water lettuce has delicate, feathery roots that extend into the water. In addition to helping the plant stay attached to the water’s surface, these roots also take up nutrients from the water column. Pistia Stratiotes
gets the nutrients it needs for healthy growth from its roots and requires a lot of light.
Frogbit, on the other hand, has a more intricate root system. Its roots spread out from the plant in all directions and are thicker and more solid. Frogbit is best suited to living in the shallow sections of a pond or aquarium since its roots are designed to grow in mud or debris.
Frogbit can thrive in lower light levels than Pistia Stratiotes and doesn’t require a steady supply of nutrients.
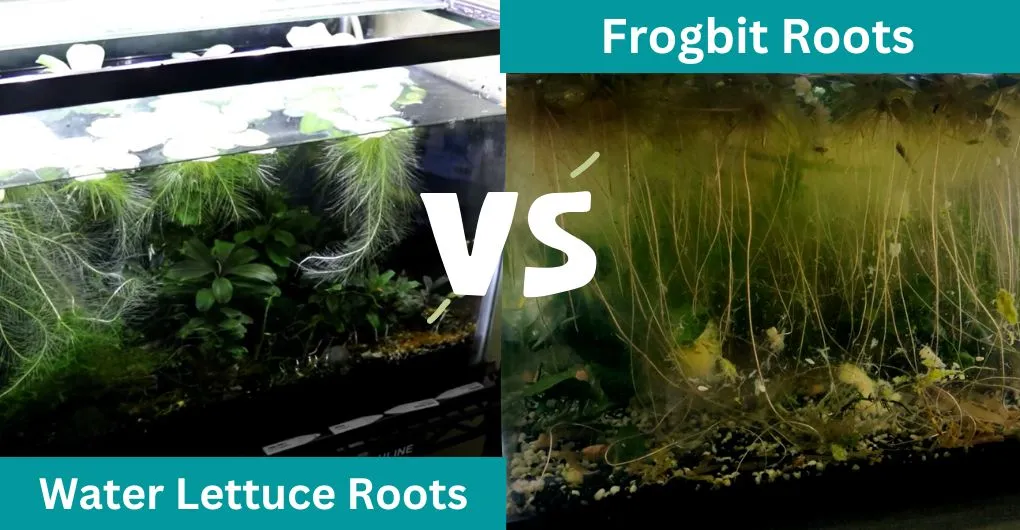
What effects do these variations in root systems have on your aquarium? Pistia Stratiotes and Frogbit are wonderful alternatives if you’re searching for a plant that will shelter and give shade to your aquatic life. Frogbit, though, would be a better option if you’re seeking a plant that can endure reduced light levels.
Additionally, Dwarf Water Lettuce may grow more swiftly and become lusher in the presence of abundant nutrients, whereas Frogbit may become more sluggish and unwell.
Dwarf Water Lettuce and Frogbit: Differences in Flowers:
Dwarf Water Lettuce produces small, yellow flowers about 1-2 centimeters in diameter. The flowers are borne on long, slender stems that are higher above the surface of water. The flowers, which are typically visible above the waterline, might bloom on separate stems at the same time.
While the leaves of Frogbit (Hydrocharis morsus-ranae) likewise form rosettes, they are smaller and less lustrous than those of Dwarf. Frogbit produces small, white flowers that are about 1 centimeter in diameter. Compared to Pistia Stratiotes, the flowers are carried on shorter stalks, but the leaves normally cover the blooms when they are present.
Pistia Stratiotes vs Frogbit: Growth Rate differences
In terms of growth, Frogbit is considered a fast-growing plant. The plant is easy to reproduce by cutting it into smaller portions and can reach its maximum height in as little as a few weeks. Although this plant is low maintenance and simple to maintain, certain environments may make it more prone to becoming invasive.
Dwarf water lettuce, on the other hand, is considered a slow-growing plant compared to Frogbit. It may take the plant several weeks or months to grow to its maximum size. Therefore, it’s essential to maintain a consistent water temperature and lighting environment to encourage healthy growth.
However, once it has grown, it can swiftly cover the surface of a pond or tank, offering shade and assisting in controlling the water’s temperature.
Dwarf water lettuce vs Frogbit: Maintenance differences
Pistia Stratiotes can be a bit picky in terms of water parameters.
- It enjoys temperatures between 66° – 80° F.
- moderate hardness
- And a pH range of 7.0 to 7.5.
As this plant needs a lot of oxygen to thrive, it’s crucial to keep a high amount of dissolved oxygen in the water. If the water quality is poor or the plant is not getting enough light, it can develop algae on its leaves.
In comparison to Pistia Stratiotes, Frogbit is significantly simpler to maintain.
- It enjoys temperatures between 64° – 86° F
- and a pH range of 6.5 to 7.5.
Frogbit is less picky about the water’s characteristics than Pistia Stratiotes and is less prone to have algae form on its leaves. However, giving it enough light is crucial because if you do not, it could grow stunted and lose its delicate beauty.
Top 7 Floating Plants for Beginners
Here’s a list of 20 floating plants that are beginner-friendly:
- Duckweed
- Water Sprite
- Salvinia
- Hornwort
- Java Moss
- Water Lettuce
- Giant Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza)
- Frogbit
- Red Root Floater
- Brazilian Waterweed
- Azolla (Azolla caroliniana)
- Star Duckweed
- Water Hyacinth
- Golden Clubmoss
- Giant Salvinia (Salvinia molesta)
- Clasping Leaf
- Anacharis
- Nile Valley
- Tape grass
- Curly Pondweed
Watch a Video on these Plants
Questions About Pistia Stratiotes
Is dwarf Water lettuce the same as Water lettuce?
Dwarf water lettuce and Pistia Stratiotes are often used interchangeably, but they are two different aquatic plants. Both plants are members of the Pistia family. Still, Pistia stratiotes has larger leaves and develops into a larger plant, while Pistia Stratiotes develops into a smaller plant.
These two plants are frequently used in aquariums and ponds to provide shade and enhance water quality because they have comparable care requirements.
Is Dwarf water lettuce good for fish?
Nile lettuce is often used as a floating plant in aquariums and ponds, providing shade and hiding places for fish. By eliminating extra nutrients and supplying oxygen via photosynthesis, it aids in enhancing the quality of the water. Additionally, fish that eat plants are able to easily consume their soft leaves.
Although Pistia Stratiotes is generally harmless for fish, it should be noted that if it spreads out of control, it can clog filters and become an annoyance. To maintain a healthy aquatic habitat for your fish, it’s essential to maintain a balance and constantly trim it.
Does Dwarf water lettuce Spread?
Pistia Statiotes does not spread quickly or abundantly, which is good news. In actuality, it develops gradually and is manageable with routine maintenance.
However, it is important to keep in mind that it can multiply if left unchecked and become invasive in certain climates. I will advise you to constantly remove any extra plant matter and trim any overgrown sections to prevent excessive growth.
Final Thoughts on Dwarf Water Lettuce vs Frogbit
Dwarf water lettuce vs Frogbit was a great lesson of discussion. To conclude this topic, I would say that both are good for creating beautiful and functional water gardens. However, personal interest also matters, so I will leave it to you to select between the two. If you have any other questions, ask me in the comments. Thank you!
Each plant has specific traits and needs for upkeep. Read my other articles to learn more:






